BRIGAID SUCCESS STORYHalophyte Zeolite Wetlands
The Halophyte Zeolite Wetlands innovation provides treatment and reuse of agro-industrial wastewaters for irrigation activities in drought prone regions.
From your point of view, how has BRIGAID contributed to the development of your innovation/company? Which specific support provided by BRIGAID was most useful to you?
The support from BRIGAID enabled MIGAL Galilee Research Institute to establish an integrated pilot system combining high cation exchange capacity substrate with succulent halophytes for improving Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) of agro-industrial effluents and thereby increase available irrigation water.
This was essential in order test the innovation in a real setting. Due to the support, the innovation progressed from technical readiness level (TRL) of 4 (laboratory tests) to a TRL of 6-7, implementation under real setting.
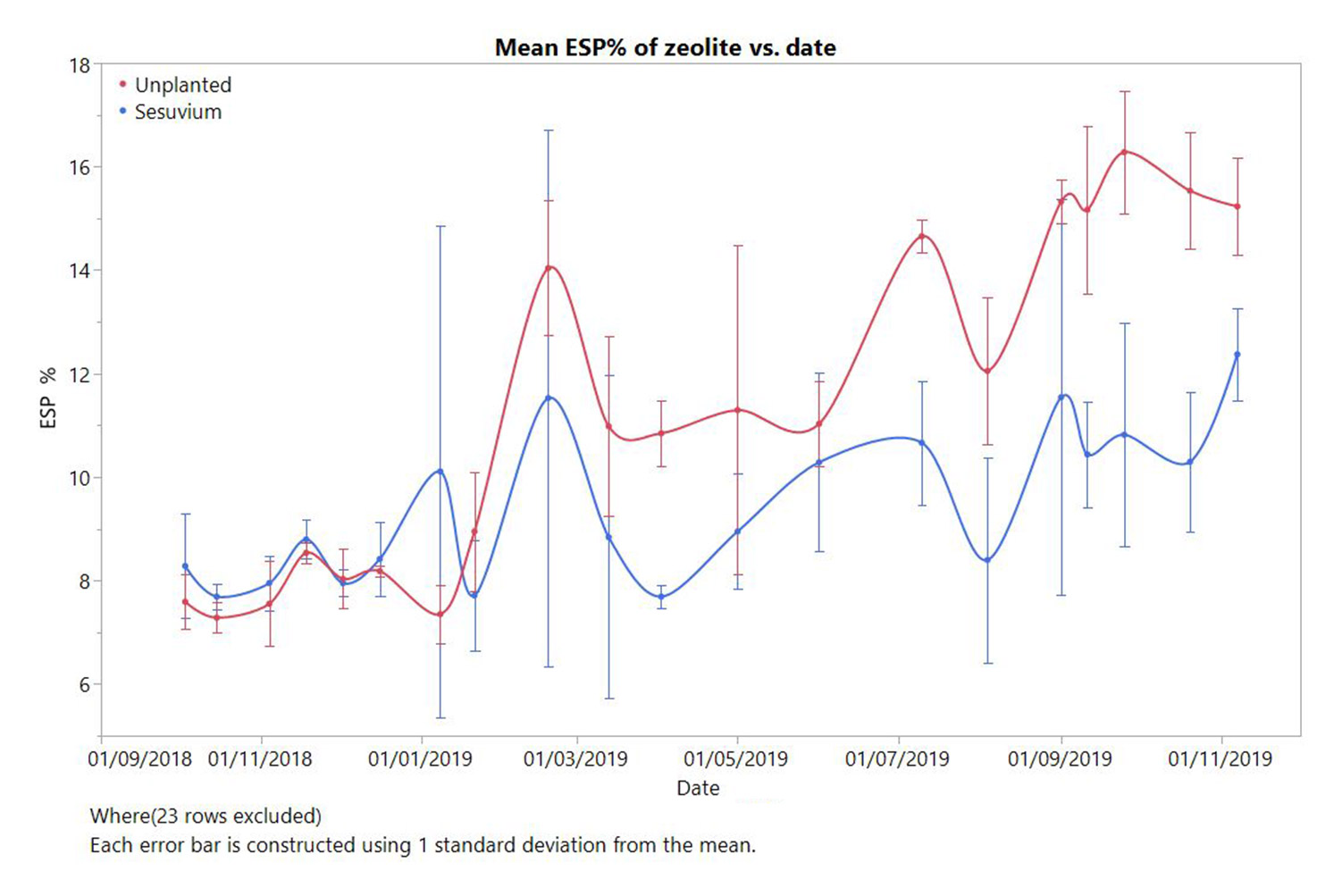
We showed that the innovation is self-sustaining, and the halophytes recondition the zeolite in-situ thereby enabling ongoing buffering of effluent SAR. Future work including modeling is necessary to establish the requisite footprint (retention time) and economic evaluation of the solution, including potentially negative effects on chloride levels due to evapotranspiration.

Please let us know about your progress and expectations after receiving support from BRIGAID,
The support from BRIGAID led to the following progress and expectations:
- Establish the conditions under which the innovation accomplishes the goal
- Submission of a manuscript to a peer reviewed journal (in review)
- As the innovation achieves more recognition (via dissemination activity of MIGAL), it may be that the combined strategy utilized in the nature-based innovation will be applied to other settings that have difficulty with high sodium levels.
Your value propositions
Commercial end-user:
Protection of irrigation water resources from influx of high Sodium Adsorption Ratio effluent (e.g. reclaimed wastewater, agro-industrial effluent). This requires additional testing in order to model the operational and economic footprint.
R&D end-user:
Expanding the concept of in-situ biological reconditioning to other active substrates.

